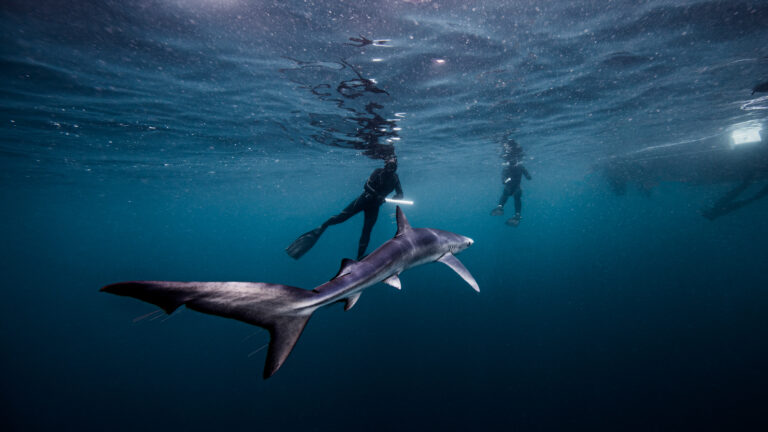
What is Open Water Certification?
Open water certification is a fundamental credential in scuba diving, signifying that an individual has achieved the necessary skills and knowledge to dive independently. This certification is recognized globally and is a prerequisite for many diving activities and advanced training courses. It ensures that divers are equipped to handle underwater environments safely and responsibly, providing a foundation for safe and enjoyable underwater adventures. Whether one seeks to dive in tropical coral reefs or cold-water kelp forests, obtaining an open water certification is the first crucial step in the journey of underwater exploration.
Historical Background
The concept of scuba diving has been around for centuries, but it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that structured training and certification programs began to emerge. The advent of modern scuba gear, including the invention of the self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA) by Jacques-Yves Cousteau and Emile Gagnan in 1943, revolutionized underwater exploration. This breakthrough made underwater breathing possible for extended periods, thus necessitating formal training and safety protocols.
In the 1950s and 1960s, as recreational scuba diving gained popularity, the need for standardized training programs became evident. Organizations like the National Association of Underwater Instructors (NAUI) and the Professional Association of Diving Instructors (PADI) were founded during this period to address this need. NAUI, established in 1959, was one of the first agencies to create comprehensive training programs for divers. PADI, founded in 1966, introduced modular training programs that made learning more accessible and flexible for aspiring divers.
These organizations played a pivotal role in developing and refining the open water certification process. They established rigorous training standards, emphasizing safety, skill proficiency, and environmental awareness. Over the years, the curriculum and training methods have evolved, incorporating advances in technology and diving practices. Today, open water certification programs are widely available, offering a structured and safe introduction to the underwater world.
Requirements for Certification
To enroll in an open water certification course, individuals must meet certain prerequisites. These typically include a minimum age requirement, which varies by organization but is generally around 10 to 12 years old. Prospective divers must also demonstrate basic swimming abilities, such as swimming 200 meters (656 feet) without stopping and treading water for 10 minutes. These requirements ensure that candidates have a fundamental level of fitness and water comfort necessary for safe diving.
The certification process involves both theoretical and practical components. The theoretical portion covers essential knowledge such as diving physics and physiology, dive planning, equipment usage, and emergency procedures. This knowledge is typically imparted through classroom sessions, online learning modules, or a combination of both. Candidates must pass a written exam to demonstrate their understanding of these concepts.
The practical component consists of confined water dives and open water dives. Confined water dives take place in a controlled environment, such as a swimming pool, where candidates learn and practice basic scuba skills. These skills include regulator recovery, mask clearing, buoyancy control, and underwater communication. Mastery of these skills in a confined setting is crucial before moving on to open water dives, which are conducted in natural bodies of water like lakes, quarries, or oceans. During these dives, candidates apply their skills in real-world conditions under the supervision of a certified instructor.
Physical requirements and medical clearance are also important aspects of the certification process. Candidates must complete a medical questionnaire to identify any health conditions that could pose risks while diving. In some cases, a doctor’s approval may be required to proceed. Overall, the requirements for open water certification are designed to ensure that divers are adequately prepared for the challenges of underwater exploration.
Course Components
The open water certification course is structured to provide a comprehensive introduction to scuba diving. It consists of three main components: classroom learning, confined water dives, and open water dives. Each component is designed to build upon the previous one, ensuring a gradual and thorough acquisition of skills and knowledge.
Classroom learning, or knowledge development, is the first component of the course. This segment covers theoretical aspects of diving, including the science behind diving, dive planning, and the use of diving equipment. Students learn about the effects of pressure on the body, how to calculate safe dive profiles using dive tables or dive computers, and how to respond to potential underwater emergencies. This theoretical foundation is crucial for understanding the principles that underpin safe diving practices.
Confined water dives are the second component of the course. These sessions are typically conducted in a swimming pool or a similar controlled environment, allowing students to practice basic scuba skills in a safe and controlled setting. During these dives, students learn essential skills such as mask clearing, regulator recovery, buoyancy control, and underwater navigation. They also practice emergency procedures, such as sharing air with a buddy and performing a controlled emergency ascent. These skills are practiced repeatedly until students can perform them confidently and competently.
The final component of the course is open water dives. These dives are conducted in natural bodies of water, such as lakes, quarries, or oceans, where students apply their skills in real-world conditions. Typically, four open water dives are required to complete the certification. During these dives, students demonstrate their ability to perform the skills learned in confined water while navigating the challenges of the open water environment. Instructors assess students’ proficiency and ensure they can dive safely and independently. Successful completion of these dives signifies that the student has met the standards for open water certification.
Certification Agencies
Several major organizations offer open water certification, each with its own approach and standards. The most widely recognized agencies include the Professional Association of Diving Instructors (PADI), Scuba Schools International (SSI), and the National Association of Underwater Instructors (NAUI). While each agency has its unique features, their certifications are generally accepted worldwide, allowing divers to dive with operators and shops globally.
PADI is the largest and most recognized scuba diving certification agency in the world. Founded in 1966, PADI has developed a comprehensive and accessible training system that includes modular learning options. This flexibility has made PADI courses popular among divers of all ages and skill levels. PADI’s certification is widely recognized, making it easy for divers to rent equipment and book diving excursions anywhere in the world.
SSI, established in 1970, is another prominent certification agency. SSI emphasizes personalized training and the use of digital learning tools, allowing students to progress at their own pace. SSI’s training philosophy focuses on building comfort and confidence through practice, with an emphasis on real-world application. SSI certifications are also globally recognized and accepted by dive operators and shops.
NAUI, founded in 1959, is one of the oldest scuba diving certification agencies. NAUI’s training programs are known for their rigorous standards and emphasis on safety and environmental awareness. NAUI instructors are given the flexibility to adapt their teaching methods to the needs of their students, ensuring a personalized learning experience. NAUI certifications are highly respected and accepted worldwide.
While each agency has its unique approach, they all adhere to internationally recognized standards for scuba training. This ensures that divers receive consistent and comprehensive training regardless of the certifying organization. The interoperability of certifications among these agencies allows divers to continue their education and pursue advanced training with any recognized agency, providing a seamless progression in their scuba diving journey.
Benefits of Obtaining Certification
Obtaining an open water certification offers numerous benefits, extending beyond the ability to scuba dive independently. One of the primary benefits is the emphasis on safety. The training ensures that divers are well-prepared to handle various underwater scenarios, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing overall safety. Certified divers are equipped with the knowledge and skills to manage potential issues, such as equipment malfunctions, adverse weather conditions, and health-related concerns.
Another significant benefit is the opportunity for skill enhancement. The certification course teaches essential scuba skills that form the foundation for more advanced techniques. With a solid grasp of basic skills, certified divers can pursue further education and specialty courses, such as underwater photography, wreck diving, and deep diving. This opens up a wide range of diving experiences and challenges, allowing divers to continually improve their abilities and explore new underwater environments.
The sense of community and camaraderie among divers is also a notable benefit of obtaining certification. Diving is often a social activity, and being part of the diving community provides opportunities to meet like-minded individuals and share experiences. Certified divers can join dive clubs, participate in group diving trips, and engage in conservation efforts. This sense of belonging and shared passion enhances the overall diving experience and fosters lasting friendships.
Moreover, having an open water certification grants access to a wider range of diving destinations and services. Many dive operators and resorts require proof of certification before allowing individuals to participate in diving activities. Certified divers can rent equipment, book guided dives, and explore dive sites that are not accessible to non-certified individuals. This opens up a world of underwater exploration, from vibrant coral reefs and shipwrecks to unique marine ecosystems.
In summary, obtaining an open water certification offers a comprehensive introduction to scuba diving, ensuring safety, skill proficiency, and access to a global diving community. It provides a solid foundation for further education and a lifetime of underwater adventures.
Challenges and Considerations
While obtaining an open water certification is rewarding, it is not without its challenges. One common challenge is overcoming initial fears and anxieties associated with breathing underwater and dealing with the unfamiliar underwater environment. Many beginners experience nervousness during their first few dives, which can affect their performance and enjoyment. However, with proper instruction, practice, and support, most divers overcome these initial challenges and become comfortable underwater.
Another challenge is the physical demands of diving. While scuba diving is generally accessible to people of various fitness levels, it does require a certain degree of physical fitness. Carrying heavy equipment, swimming against currents, and managing buoyancy can be physically demanding. It is important for prospective divers to assess their fitness levels and consult with their instructors or doctors if they have any health concerns.
Choosing the right certification agency and instructor is another important consideration. Different agencies offer various teaching styles and course structures, and the quality of instruction can vary. Prospective divers should research their options, read reviews, and
speak with experienced divers to find a reputable instructor or dive center. A good instructor can make a significant difference in the learning experience, providing personalized attention and fostering a positive and safe learning environment.
Environmental and ethical responsibilities are also key considerations for divers. Open water certification courses often emphasize the importance of protecting marine ecosystems and practicing responsible diving. Divers are taught to avoid touching or disturbing marine life, practice good buoyancy control to prevent damage to coral reefs, and adhere to local regulations and guidelines. Being mindful of these responsibilities is crucial for preserving the underwater environment for future generations.
Overall, while there are challenges and considerations involved in obtaining an open water certification, they are outweighed by the rewards. With proper preparation, a positive mindset, and a commitment to responsible diving, these challenges can be successfully navigated, paving the way for a fulfilling and safe diving experience.
Key Takeaways
Open water certification is a foundational credential that provides individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to safely and independently explore the underwater world. It involves a combination of theoretical learning, practical skill development, and real-world application through confined and open water dives. Certification offers numerous benefits, including enhanced safety, skill development, and access to a global diving community. Despite challenges, such as overcoming initial fears and physical demands, the rewards of certification make it a valuable and enriching experience for anyone interested in scuba diving.